Diagnostics and monitoring of transformers: fault prevention
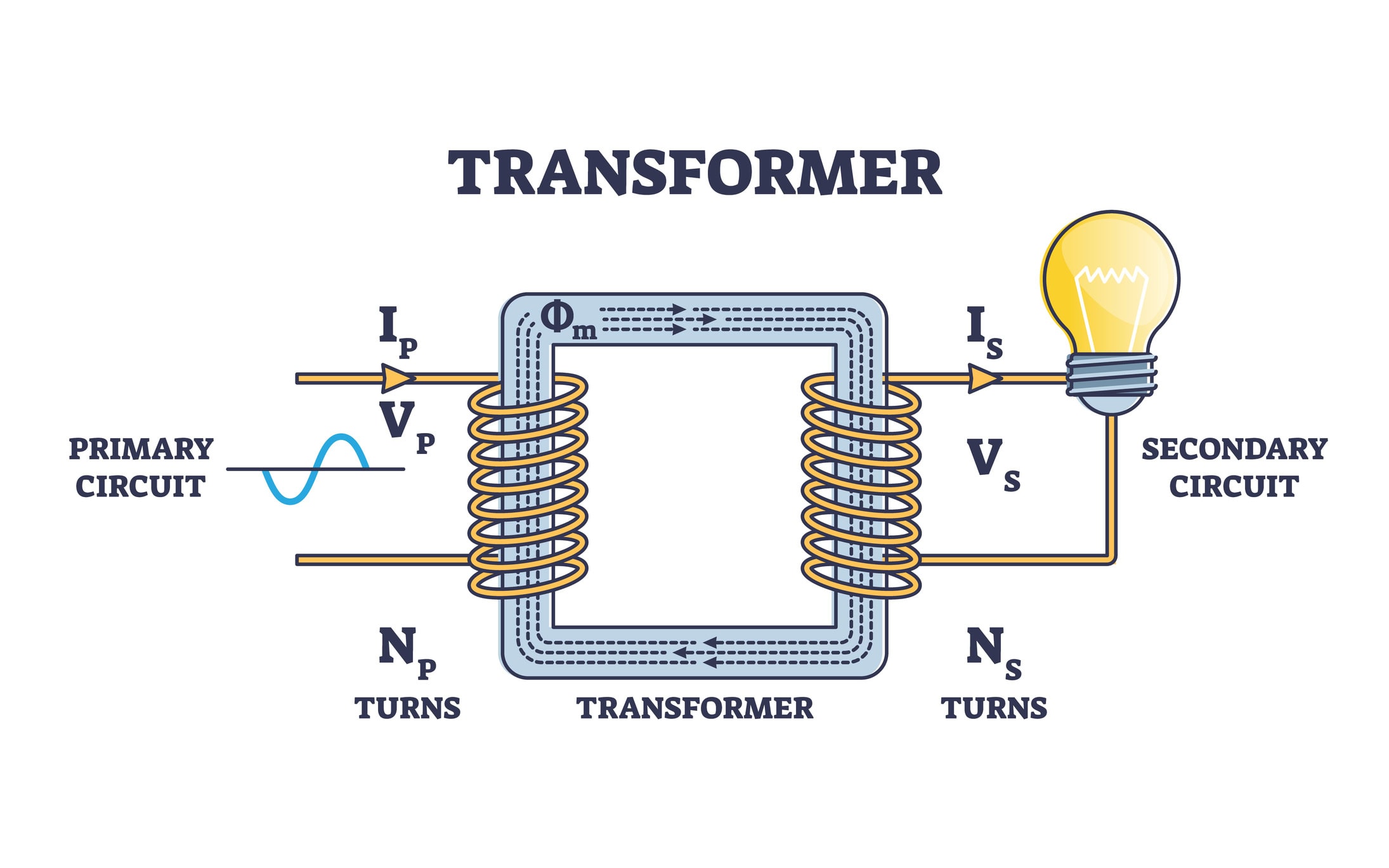
In the modern power environment, where more and more emphasis is being placed on efficiency and continuous operation, transformer monitoring is becoming a necessity. Diagnostic systems therefore reflect the specific needs of each type of machine, from conventional oil-immersed to special transformers.
Why is transformer monitoring important?
In the past, maintenance was carried out reactively, that is, only when a problem arose was it dealt with. However, the present requires a predictive approach. However, modern technology allows us to “see inside” the machine without having to shut it down. Real-time monitoring of transformers can therefore identify up to 90% of incipient faults in their embryonic stage, extending the life of the equipment by decades.
Tailored diagnostics: from oil to renewables
Oil Transformers
For oil-immersed transformers, the key indicator of the condition is the insulating liquid. The gases dissolved in the oil are analyzed. The presence of specific gases (hydrogen, methane, acetylene) accurately indicates the type of fault, from electrical discharges to thermal overload. The water content of the oil is also monitored. This is critical for maintaining dielectric strength and preventing degradation of the paper insulation.

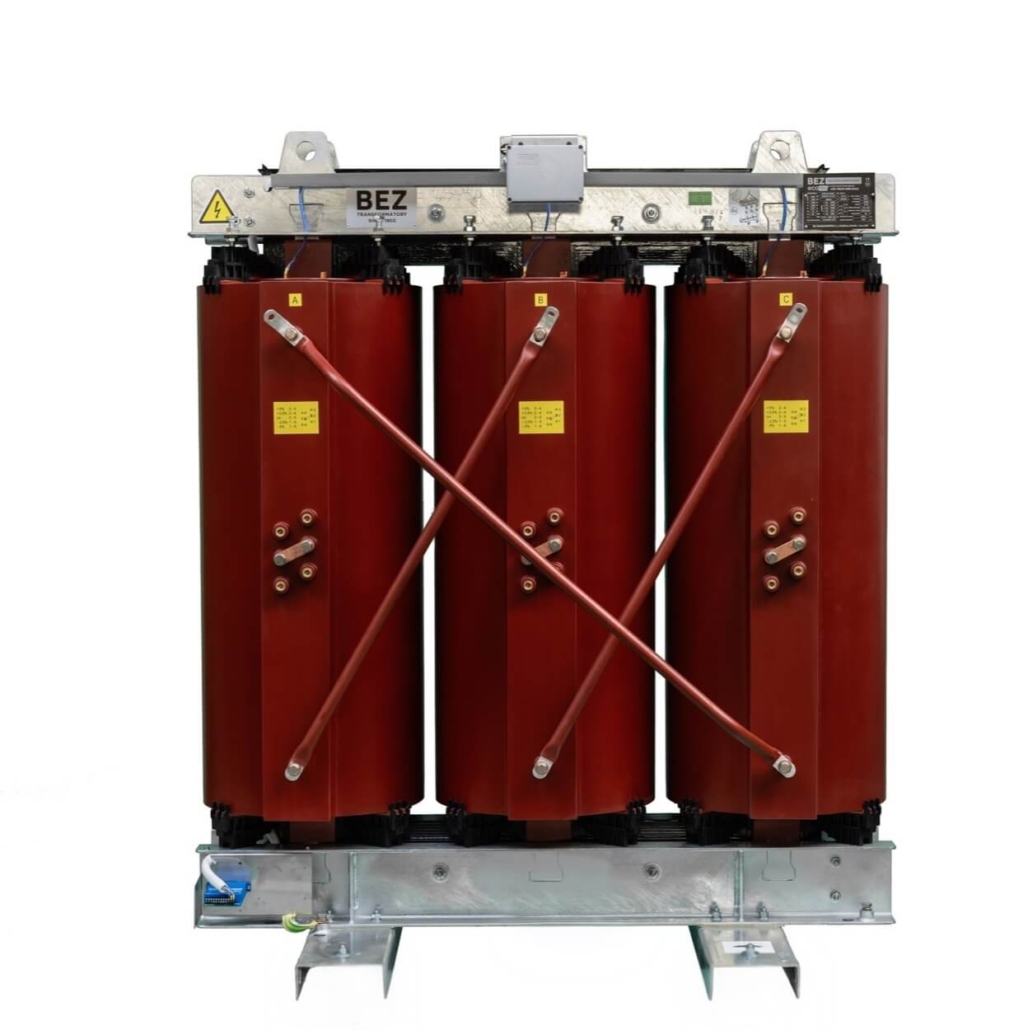
Dry transformers
Dry transformers, insulated with epoxy resin, are ideal for areas with high fire safety requirements. Monitoring of thermal points is important. Using PT100 or fibre optic sensors, the winding temperature is monitored in real time, preventing thermal degradation of the resin. Partial discharge measurements are also an effective method. This method detects in time micro-cracks in the insulation that could lead to a fatal short circuit.

Special transformers
In industrial plants, transformers face high current surges and harmonic distortion. Therefore , we analyze the mechanical vibration. We monitor the stability of the core and windings, which are stressed by dynamic forces. We do not neglect the monitoring of tap changers. Monitoring the condition of the contacts directly under load eliminates the risk of mechanical failure.
Transformers for renewable energy
Photovoltaic and wind power plants present a new challenge for transformers due to cyclical and unstable loads. Adaptive monitoring is important. Our RES systems take into account frequent temperature fluctuations and variable power output to optimize the operation of substations in smart grids.
Benefits of systematic monitoring of transformers for operation
The introduction of modern diagnostic methods is not just about technical measurements, but about strategic asset management. The correct interpretation of data brings many benefits to operators:
- Reduce operating costs: it allows you to switch to targeted service based on actual status instead of fixed time revisions, which can be inefficient.
- Investment optimisation: accurate data on wear rates and residual lifetime allows managers to better plan infrastructure renewal and avoid premature purchases of new machines.
- Enhancing safety and ecology: continuous monitoring minimizes the risk of catastrophic failures, fires or environmental accidents associated with oil spills.
In today’s power industry, investing in transformer monitoring is a necessary step to ensure business continuity. At a time of long lead times for new technologies and high energy costs, keeping existing infrastructure in tip-top shape is the most effective route to grid sustainability and stability.