How the transformer works: a simple explanation for everyone
Even if you don’t know how a transformer works, it would be hard to imagine your life without one. Yet many people don’t know what it is and how it actually works. That’s why today we’ll explain the principle of its operation in a simple and understandable way. We will look at the basic processes that take place in it and show you its practical use.
The principle of operation of the transformer
The transformer changes the electrical voltage. It can either increase or decrease it. Its basic parts include coils of aluminum or copper wire, called primary and secondary windings. Between them is a metal core, usually made of mild steel.
When an alternating electric current is applied to the first coil (primary winding), a magnetic field is created around it. This magnetic field travels through the metal core of the transformer to the second coil (secondary winding) where the changing magnetic field “touches” the conductor and causes a new electric current to appear in it. This is called induction. Depending on how many turns the second coil has compared to the first, the voltage will either increase or decrease.
This phenomenon is described by Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, which states that “a change in the magnetic field over time induces an electric voltage in the coil”. This means that the transformer only works with alternating current because direct current would not create the changing magnetic field needed for induction.
This way the transformer changes voltage without anything moving in it. The whole process is based on a magnetic field and alternating current.
How the transformer and its individual parts work
The transformer has two main windings. The primary winding is the part that receives the electric current from a source such as a power plant. The secondary winding passes the treated voltage to where we need to get it, for example to household appliances. The two windings are wound from copper or aluminium wires and separated from each other so that the electric current cannot flow directly, but only through the magnetic field in the core.
The core is a metal part, most often made of steel or iron, which is placed between the windings. Its function is to conduct the magnetic field generated in the primary winding to the secondary winding. Thanks to the core, the magnetic field is concentrated and the transformer operates efficiently.
Types of transformers
In practice, we encounter various types of transformers, which differ in design and application:
- Dry transformers have an air-cooled core and windings. They are mainly used indoors or where cleanliness and safety are important, such as in hospitals or offices. They are more environmentally friendly as they do not contain oil, but have lower maximum outputs.
- Oil Transformers are filled with insulating oil, which helps to cool the windings and insulate them at the same time. They are mainly used in large substations and high power applications as the oil improves heat dissipation and reduces the risk of overheating.
- There are also special transformersthat are designed for specific purposes, for example, interconnecting, three-winding, inverter, single-phase, excitation or earthing transformers.
- Many are also adapted to work with solar panels, wind turbines or other sources. Transformers for renewable energy sources supply electricity with specific parameters and help to connect these sources to the grid correctly.
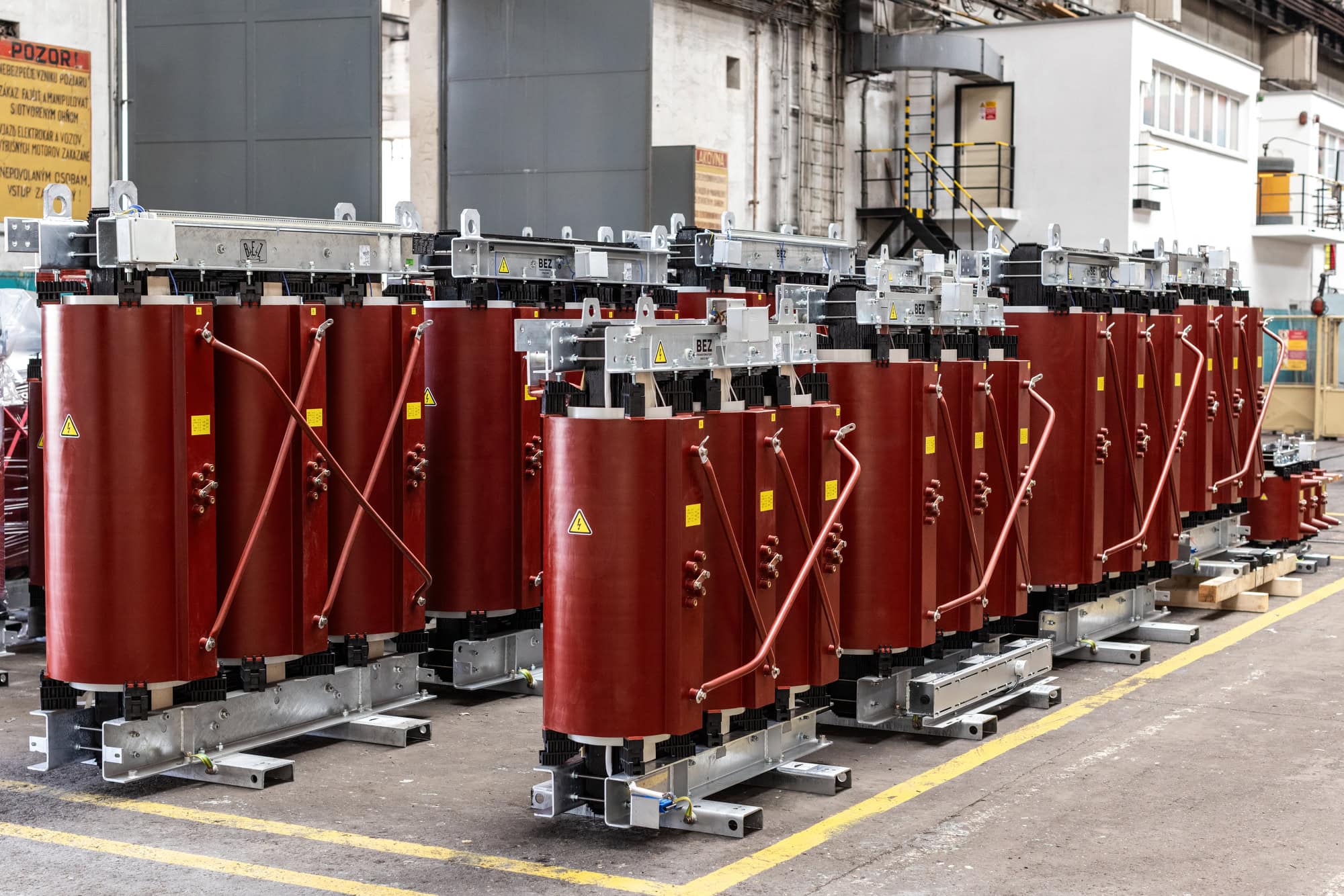

Practical use of transformers in electrical networks
Transformers safely and efficiently transmit electricity from power stations to our homes. This is because electricity is generated in large, high-voltage power stations to minimise losses in long-distance transmission. However, when it comes closer to where we want to use it, substations have to reduce its voltage to a level that is safe for homes or industry. This allows us to plug in appliances such as a TV, computer or fridge at home without worrying about anything going wrong.
BEZ TRANSFORMÁTORY, we could not…
… use common household appliances, as most of them need low voltage.
… to transmit electricity over long distances without huge losses.
… to work safely with high voltage in industry or power industry.
Understanding the basic principle of how a transformer works helps us to better understand how important these devices are in our daily lives. Even if we don’t see them, modern society could not function without them.









