Transformation ratio: how it works and why it is important
In order for a transformer to effectively change the voltage between different parts of the network in electricity transmission and distribution systems, it must have a well-defined transformation ratio (also called transformer conversion). This is a fundamental parameter of any transformer. It determines how the voltage changes between its input and output, i.e. between the primary and secondary windings.
Transformation ratio
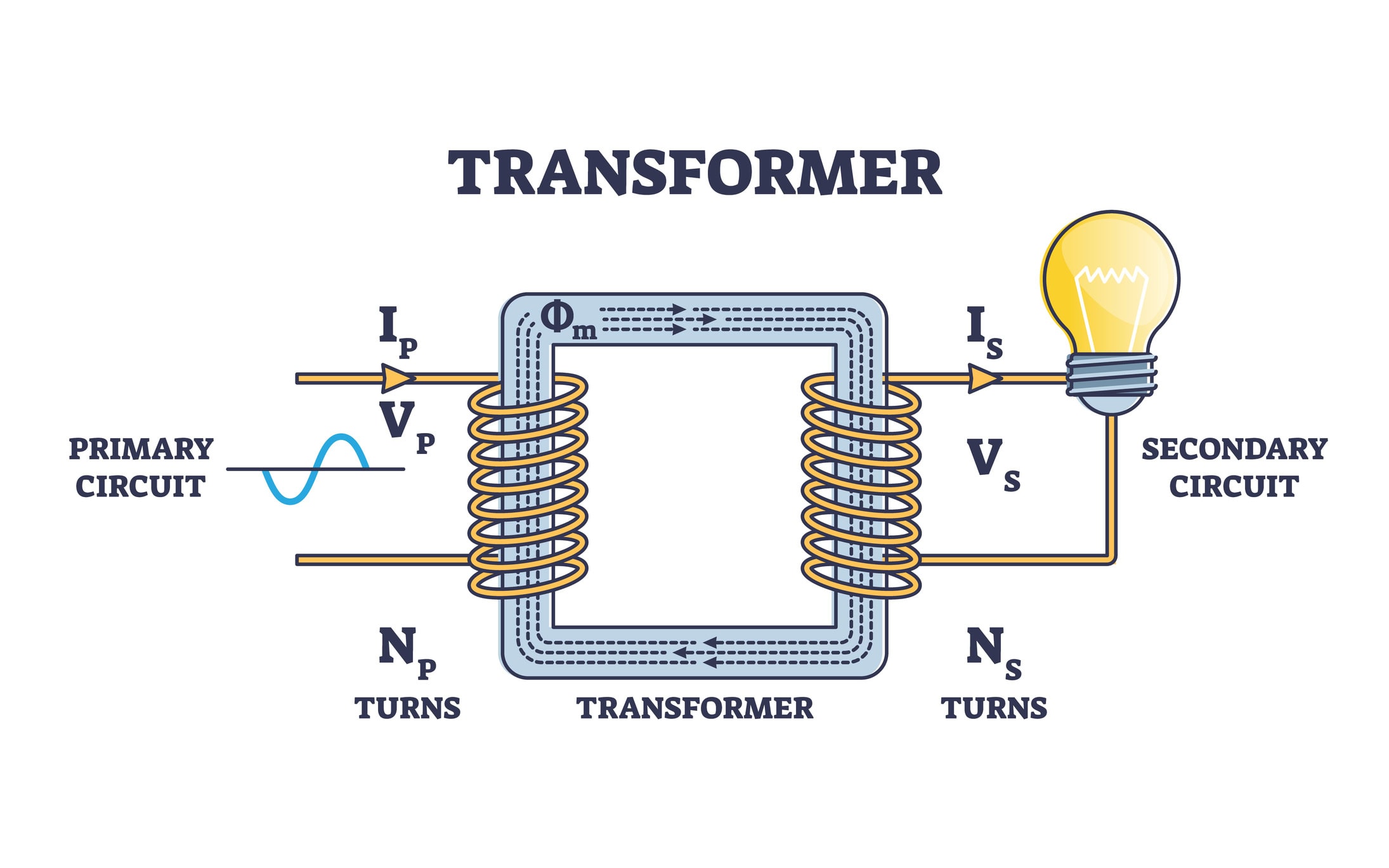
The transformation ratio represents the ratio between the number of turns on the primary coil and the number of turns on the secondary coil of the transformer. It determines how the electrical voltage changes as it passes through the transformer. It is denoted by the letter k . In practice, it is often also referred to as the ratio of input to output voltage.
Two basic types of transformers according to transformation ratio
The transformation ratio is a basic indicator of how a transformer adapts its electrical parameters to the requirements of a particular device or network:
- Step-down transformer (k > 1): it is used to reduce the voltage. An example is an adapter that converts 230 V to 12 V for household appliances.
- Step-up transformer (k < 1): used to increase the voltage, for example when transferring electricity from sources to grids.

For decades, BEZ TRANSFORMÁTORY has been manufacturing quality transformers that accurately reflect the requirements for the correct transformation ratio from distribution networks to industrial applications.
See our current offer or contact us for a customized transformer design.
How is the transformation ratio calculated?
The calculation of the transformation ratio is simple. As we have already indicated, the transformation ratio is expressed either by the number of turns on the windings or by the voltages. The two expressions are mathematically equivalent: k = U₁ / U₂ = N₁ / N₂, where:
- k = transformation ratio
- U1, U2= voltages on primary and secondary windings
- N1, N2= number of turns on primary and secondary windings
Transformation ratio and its importance in practice
The correct setting of the transformation ratio has a major impact on the operation of electrical equipment and entire distribution networks:
- Efficient power transmission: in long-distance power transmission, voltage boosting is used with the help of transformers with a low transformation ratio. This makes it possible to reduce the current and thus the line losses. For distribution to households, the voltage is again reduced using step-down transformers.
- Voltage adaptation for different equipment:With the right transformation ratio, we can adapt the output voltage of electrical equipment so that it operates safely and reliably.
- Measurement and protection systems:Current and voltage transformers enable high voltage currents to be monitored safely by transforming them into smaller measurable values using a precisely defined transformation ratio.
- Industrial and special applications: Special transformers with atypical transformation ratios are often used in industry . They allow specific voltage levels for machines, lines or laboratory instruments. This is because without the correct transformation ratio setting, these devices would not be able to function.

The transformation ratio is therefore a key parameter of any transformer and determines how the voltage between the input and output of the device changes. Its correct understanding and calculation are essential in the design, set-up and safe operation of electrical systems.
If you are looking for a reliable partner for the design and manufacture of customized transformers, take a look at the offer of BEZ TRANSFORMÁTORY, a leader in power solutions.








