Transformer parts: key components and their role in electricity distribution
BEZ transformátory, it would not be possible to transmit electricity efficiently over long distances. Significant losses would occur. But what are the key components that change the AC voltage and enable the efficient transmission and distribution of electricity? What are the parts of a transformer and what is their function in operation?
Core: the heart of the transformer
The core is the key element of the transformer. It serves to conduct the magnetic flux between the primary and secondary windings, thus ensuring efficient energy transfer through electromagnetic induction. It focuses and amplifies the magnetic field created by the current in the windings. The better quality material it is made of, the more it minimizes energy losses and increases the efficiency of the transformer.
The core is usually made of thin sheets of electrical steel with an insulating layer. The sheets are layered to reduce eddy currents and hence heat loss. This material is chosen for its excellent magnetic properties – in particular low hysteresis loss and high magnetic permeability.
According to the arrangement of the magnetic flux in the core, we distinguish two basic types of core design:
- Core (column) core: The windings are placed on the arms of the core and the magnetic flux passes mainly through the columns. This type of core is simpler and is often used in power applications.
- Core cladding: the windings are surrounded by a core on all sides, resulting in lower dissipation losses and higher mechanical resistance. This arrangement is suitable, for example, where there are requirements for compactness and strength.
The choice of core type depends on the requirements of the specific application, such as current magnitude, voltage, dimensions and cooling conditions.
Windings: a key element in voltage transformation
Windings are among the key parts of the transformer. They are coils wound on a core and, based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, they enable the transfer of electrical energy between circuits.
Most often in the transformer we find:
- Primary windingsthat receive electricity from the grid and create magnetic flux in the core.
- Secondary windings that induce an electrical voltage according to the turns ratio and supply it to the output circuit.
Transformers with a more complex structure may also have a tertiary winding, auxiliary winding or balancing winding.
Windings are made of copper or aluminium conductor:
- Copper ones have better conductivity, lower losses, but higher price.
- Aluminium ones are a cheaper alternative, but have a larger size and higher resistance.
The insulation of the windings is also important . Different materials are used, for example varnish, paper, polyester film or epoxy resin.

Windings play a key role in the proper function of a transformer because they determine the output voltage and the efficiency of power transfer. If the secondary winding has more turns than the primary, the transformer voltage increases. Conversely, if the secondary winding has fewer turns than the primary, the transformer reduces the voltage. Thus, we speak of step-up and step-down transformers.
Transformer cooling parts
Each transformer generates heat during operation. If it were not sufficiently cooled, the temperature would rise dangerously, causing, for example, insulation degradation, reduced efficiency and, in extreme cases, equipment failure. Choosing the right cooling system is therefore very important:
- Olejové chladenie: Efektívne odvádza teplo a predlžuje životnosť zariadenia. Nájdeme ho vo veľkých výkonových transformátoroch v elektrárňach a rozvodných sieťach alebo priemyselných transformátoroch, kde je potrebná vysoká účinnosť.
- Vzduchové chladenie: Je menej náročné na údržbu a ekologicky prijateľnejšie. Používa sa v malých a stredných distribučných transformátoroch v mestských budovách, ale aj nemocniciach, kancelárskych priestoroch a tuneloch, kde je na prvom mieste bezpečnosť. Nehrozí totiž žiadne riziko úniku oleja.
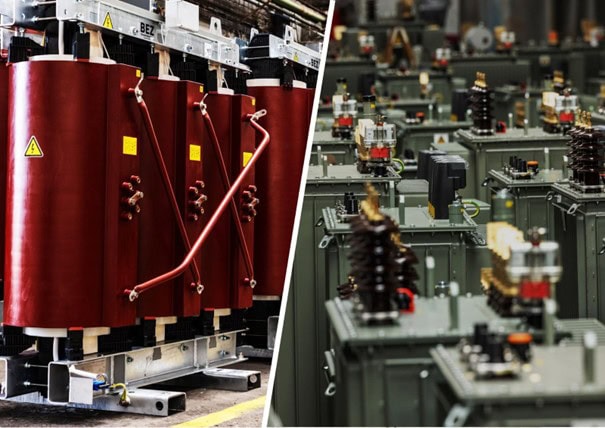
Other transformer parts important for safe and efficient operation
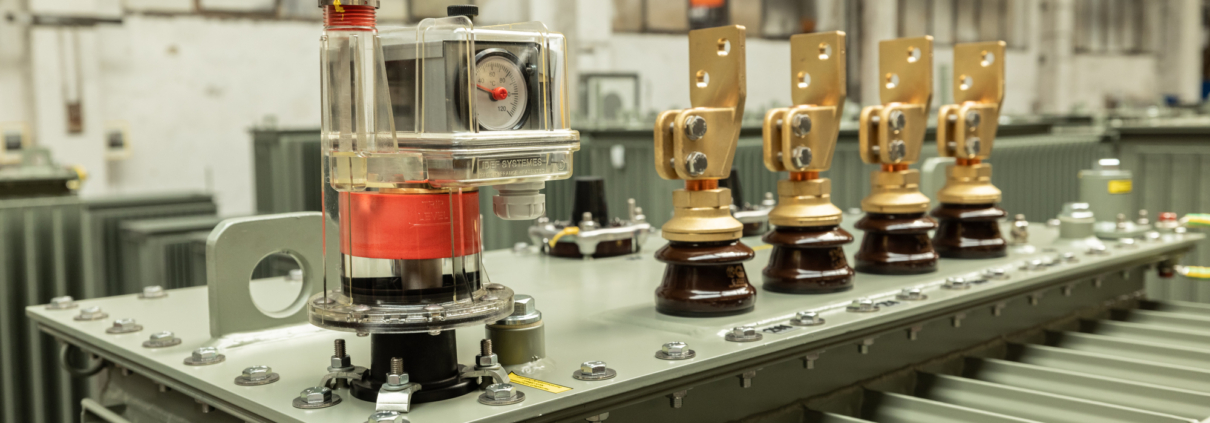
In addition to the main parts such as the core, windings and cooling systems, the transformer is equipped with various accessories that enhance its reliability, safety and functionality and help protect the transformer from damage. They also facilitate its maintenance and ensure proper operation:
- Electrical safety is enhanced by insulators that separate the electrical conductors from the transformer carcass and prevent electrical short circuits (jumps).
- Reliable power transmission is ensured by the connection terminals used to connect the transformer to the power grid.
- To protect against overload, the transformer is usually equipped with a monitoring device. In the case of oil-immersed transformers, also an overpressure valve which, in the event of overload or short circuit, if not detected by other protections, will protect the transformer from damage.
- The tap changers allow the output voltage to be adjusted according to the current network conditions. They keep the voltage stable and increase the efficiency of the device.
- Excessive pressure inside the transformer is prevented by an expansion tank that compensates for changes in oil volume caused by temperature fluctuations.
- Early detection of problems such as oil leaks or overheating is detected early by oil level and temperature indicators.
Only the proper functioning of these components will ensure safe and efficient operation. They help prevent outages, extend the life of the equipment and ensure a stable supply of electricity.

Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!